Parler
Parler Gab
Gab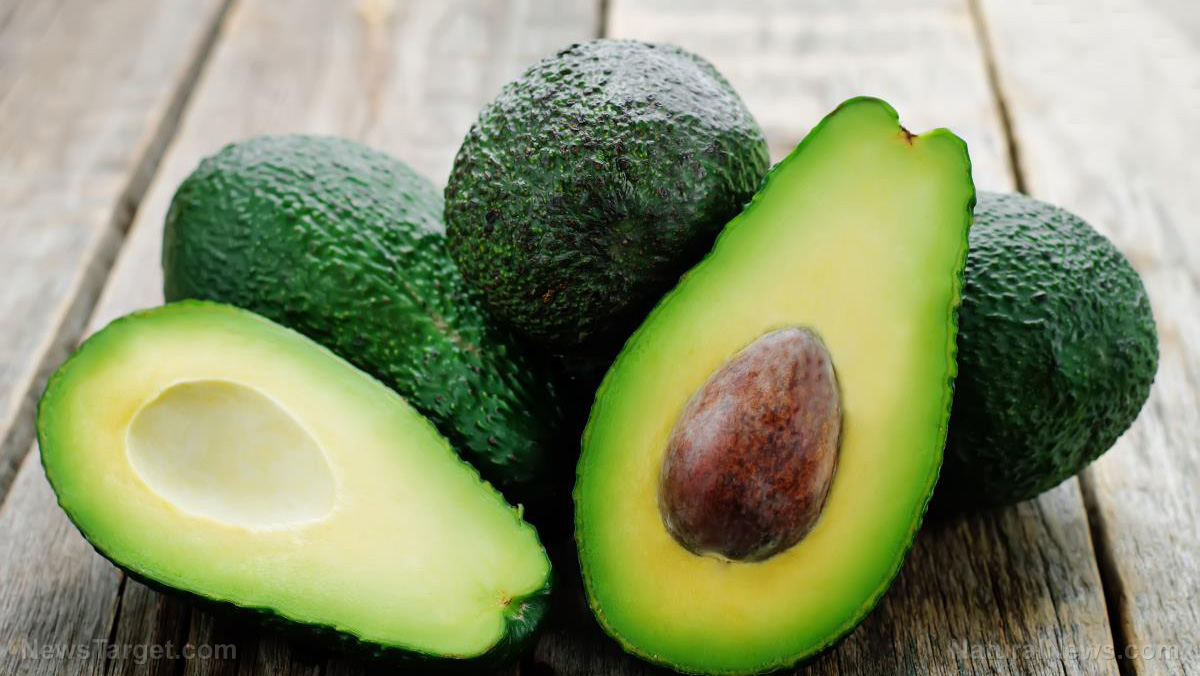
"The avocado intervention increased MPD by more than double that of the supplement, with only a small fraction of the amount of lutein. This suggests that other components in avocado are particularly effective in the enrichment of neural lutein. The most likely components are monounsaturated fatty acids."
3. Less Belly Fat Eating avocados is associated with lower abdominal obesity, less weight gain and reduced risk of being overweight or obese.[viii] Among 105 adults who ate a meal with a daily avocado or a similar meal without avocado for 12 weeks, women in the avocado group had a greater reduction in visceral adipose tissue (VAT) and the ratio of VAT to subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue, known as the VS ratio.[ix] This beneficial change could indicate a lower risk of related diseases:[x]"Relative to other adipose tissue depots, VAT accumulation, surrounding internal organs such as the liver, is associated with type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, inflammation, increased risk of thrombosis, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Therefore, the decrease in VS Ratio among treatment group participants suggests that avocado intake imparts a beneficial abdominal adiposity profile."
For reference, eating a daily avocado for 12 weeks led to an approximately 5% reduction in VAT among the women. A 26% reduction in VAT over 12 months has previously been linked to improvements in cardiorespiratory fitness, inflammation, lipid profiles and glucose tolerance. "It is possible," the team said, "that maintaining the treatment regimen [eating an avocado a day] over the course of a longer period could have provided the necessary cumulative reduction in VAT to be clinically meaningful."[xi] 4. A Healthier Heart Consuming a healthy diet with an avocado added daily for five weeks had a positive effect on markers of heart health, including decreased circulating oxidized LDL in overweight and obese adults.[xii] High concentration of oxidized LDL is a risk factor for heart disease. Consuming an avocado a day was also linked to a reduction in small, dense LDL particles, which are susceptible to oxidation and also linked to an increased risk of heart disease. Over the five-week period, a daily avocado decreased plasma oxidized LDL by 8.8%, the study found, along with increasing plasma lutein concentrations. "We conclude that these benefits are due to the bioactive compounds present in avocados beyond their fatty acids," the team noted.[xiii] More Reasons to Eat Avocados When you browse through our avocado research database, you'll see that avocados may benefit 46 diseases, from psoriasis and osteoarthritis to breast cancer and colitis. With 35 known pharmacological actions -- including antifungal, hypoglycemic and antiulcer properties, for instance -- avocados are one tasty treat you can feel good about indulging in. Add them to your smoothies, eat them alongside eggs for breakfast or use them to make guacamole. No matter how you consume them, be sure this satisfying superfood makes a regular appearance on your menu. Read more at: GreenMedInfo.comA MAGA siege of the Democrats’ deep state
By News Editors // Share
We are closer to all-out war in Europe, in Asia, and in the Middle East than most people realize
By News Editors // Share
Revolutionize your diet with pomegranate: The miracle juice for gut health and metabolism
By Willow Tohi // Share
Could camel milk be a game-changer for autism? Science says it’s worth exploring
By Olivia Cook // Share
Governments continue to obscure COVID-19 vaccine data amid rising concerns over excess deaths
By patricklewis // Share
Tech giant Microsoft backs EXTINCTION with its support of carbon capture programs
By ramontomeydw // Share
Germany to resume arms exports to Israel despite repeated ceasefire violations
By isabelle // Share