Parler
Parler Gab
Gab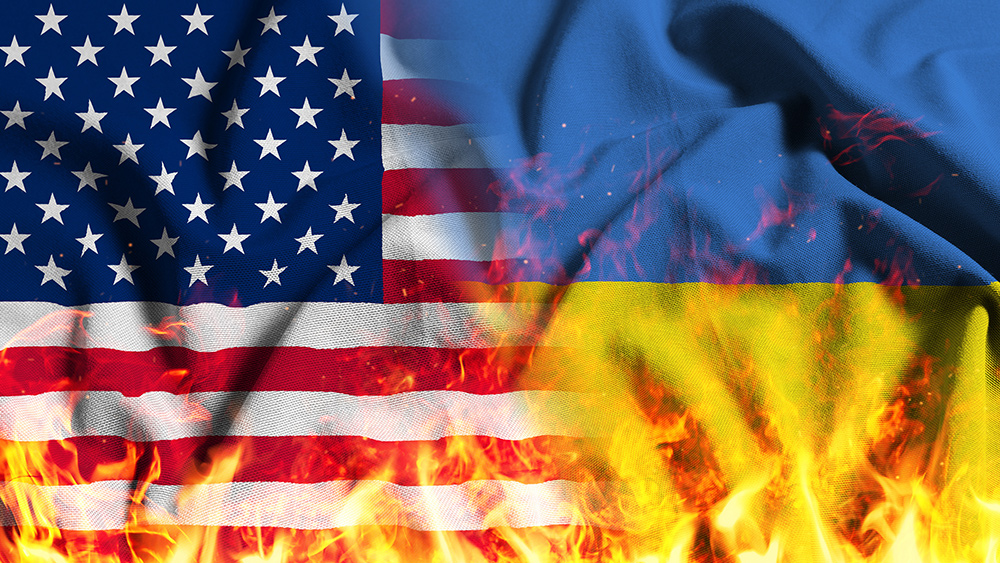
- With just one hour to decide, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky rejected a U.S. proposal to gain access to Ukraine’s rare earth mineral reserves in exchange for billions in military aid.
- The proposal was presented during U.S. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent’s visit to Kyiv last week and discussed at the Munich Security Conference over the weekend.
- U.S. President Donald Trump and other U.S. officials have been pushing for the deal, while Zelensky has repeatedly deferred or refused.
- Discussions took place in Kyiv and Munich, with implications for Ukraine’s resource-rich territories.
- The deal highlights the strategic importance of rare earth minerals for technology, defense, and energy, as well as the delicate balance of U.S. aid and Ukrainian sovereignty.
A contest over critical minerals and sovereignty
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky has firmly rejected a U.S. proposal to grant Washington access to Ukraine’s rare earth mineral reserves in exchange for military aid, upping the stakes in an already complex geopolitical tug-of-war. According to reports from The Economist, The Washington Post, and Reuters, the proposal was first presented to Zelensky during a visit by U.S. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent last week. Zelensky, however, has repeatedly deferred or outright rejected the deal, signaling a reluctance to cede control over Ukraine’s natural resources to foreign powers. The proposed deal, which reportedly grants the U.S. rights to 50% of Ukraine’s mineral reserves, emerged during tense negotiations amid the ongoing conflict with Russia. U.S. President Donald Trump has openly stated that he wants Ukraine to “pay back” the estimated 300 billion in aid provided since 2022 by offering the equivalent of 500 billion worth of rare earth minerals. These minerals, which include lanthanum, cerium, and neodymium, are essential for technologies ranging from batteries and nuclear power to advanced weaponry.Misaligned expectations and strategy
Zelensky’s refusal to sign the deal during the Munich Security Conference last weekend underscores a fundamental disconnect between Kyiv and Washington. While U.S. officials view the proposal as a means of recouping investments and securing long-term strategic interests, Zelensky is advocating for a more equitable partnership. In October 2024, Zelensky unveiled his so-called “victory plan,” which included a proposal for joint use of Ukraine’s critical resources with the U.S., contingent on continued military assistance and strategic deterrence. However, at Munich, he emphasized that Ukraine was not yet ready to commit to such a deal, seeking better terms that align with the country’s sovereignty and economic interests. “This is not about who gets what,” Zelensky reportedly told reporters at the conference. “It’s about creating a partnership that respects Ukraine’s independence and ensures a sustainable future for our people.”A chess game of resources and alliances
Ukraine is home to some of the world’s most valuable mineral reserves, including Europe’s largest deposits of titanium and lithium, as well as significant amounts of beryllium, manganese, and uranium. These resources are not only vital for modern industries but also serve as a potential lifeline for Ukraine’s war-torn economy. However, roughly 20% of Ukraine’s mineral-rich territories are currently under Russian control, including the resource-rich Donbass region. Forbes estimates that $7 trillion worth of Ukraine’s mineral wealth is located in areas now administered by Russian-backed authorities in Donetsk and Lugansk. Russia has been swift to condemn the U.S.-Ukraine deal as a violation of Ukrainian sovereignty. Kremlin spokesperson Dmitry Peskov dismissed the proposal as a “commercial transaction,” arguing that such arrangements risk compromising Ukraine’s independence. “Why not just stop the aid altogether?” Peskov said in a press briefing. “If the United States is willing to tie Ukraine’s future to such one-sided deals, perhaps it’s better to let the conflict resolve itself.” Meanwhile, U.S. officials have hinted at a willingness to deploy troops to secure the rare earths, a move that could further escalate tensions in the region. As the conflict enters its third year, the debate over Ukraine’s rare earths highlights the intersection of national sovereignty, economic strategy, and military aid. For the U.S., the deal represents a pathway to secure critical resources and ensure a return on its substantial investment in Ukraine’s defense. For Kyiv, it is a matter of preserving national autonomy and fostering a sustainable post-war economy. In the end, this clash over resources is less about dollars and cents than it is about power and influence. As Zelensky continues to navigate the complexities of this high-stakes negotiation, one thing is clear: the outcome will shape not only Ukraine’s future but also the broader geopolitical landscape for years to come. And as the chess pieces continue to shift, the question remains: Will Ukraine’s rare earths prove to be the key to its salvation—or its undoing? Sources include: RT.com RT.com RT.comGOP advances Trump’s tax cuts and border agenda in dramatic 217-215 House vote
By Cassie B. // Share
Trump’s $5 million “gold card” visa plan could erase U.S. national debt
By Cassie B. // Share
Putin offers rare earth minerals deal to U.S. amid Ukraine war tensions
By Cassie B. // Share
Texas rancher slain by cartel IED near border: A call for vigilance and action
By Willow Tohi // Share
The sky’s the limit? Shanahan and Trump demand answers on geoengineering and public health
By Willow Tohi // Share
What will the Trump wrecking ball hit next?
By News Editors // Share
Governments continue to obscure COVID-19 vaccine data amid rising concerns over excess deaths
By patricklewis // Share
Tech giant Microsoft backs EXTINCTION with its support of carbon capture programs
By ramontomeydw // Share
Germany to resume arms exports to Israel despite repeated ceasefire violations
By isabelle // Share