From cognitive protection to immune support here are five compelling reasons to incorporate sweet potatoes into your everyday diet
(Article republished from
GreenMedInfo.com)
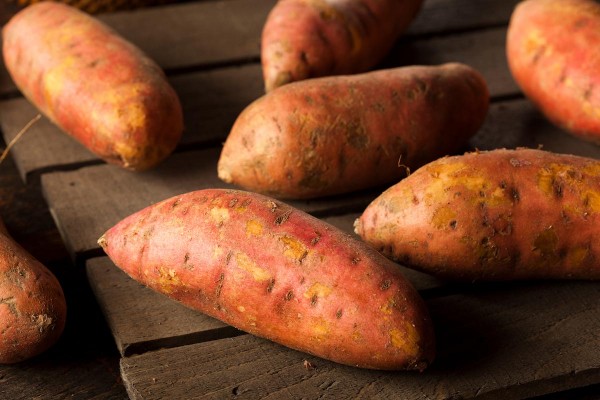
Sweet potatoes are more than just a popular staple food serving as a sweet appetizer, side dish or filling snack on their own. This starchy root vegetable has plenty to offer when it comes to achieving optimal health. Sweet potato is a common food source for many indigenous populations in Africa, Central and South Americas, the Caribbean and Hawaii.
[i]
It's an excellent source of natural compounds, including beta-carotene and anthocyanins. The high concentration of these compounds in the root crop, paired with its stable colors, make sweet potato a healthful alternative to synthetic coloring agents in food. Let's take a closer look at five ways that sweet potatoes benefit overall wellness.
1. Rich Nutrition Profile
One cup of cubed sweet potatoes provides the following:
[ii]
|
Water -- 103 grams (g)
|
Energy -- 114 kilocalories (kcal)
|
Protein -- 2.09 g
|
|
Carbohydrate -- 26.9 g
|
Fiber -- 3.99 g
|
Sugar -- 5.56 g
|
|
Calcium -- 39.9 milligrams (mg)
|
Iron -- 0.811 mg
|
Potassium -- 448 mg
|
|
Phosphorus -- 62.5 mg
|
Sodium -- 73.2 mg
|
Vitamin C -- 3.19 mg
|
The orange and
purple varieties are rich in
antioxidants such as beta-carotene, chlorogenic acid and vitamin C.
[iii],[iv] There's an abundance of colors of sweet potatoes worldwide, including white, yellow, orange and purple. In the American market, however, sweet potato typically has a deep-orange flesh color, a skin color of light to medium rose, copper or red, a sweet flavor and moist texture.
[v]
2. Enhanced Memory and Cognitive Health
A 2013 study found that a purple sweet potato extract rich in caffeoylquinic acids led to a neuroprotective effect on the brain of animal models, potentially helping improve spatial learning and memory.
[vi]
Purple sweet potato color comes from a class of naturally occurring
anthocyanins that have strong antioxidant and neuroprotective activity.
[vii] In animal subjects, it showed great promise in improving cognitive function. In further animal studies, purple sweet potatoes were shown to protect the brain by reducing inflammation.
[viii]
3. Immune Support
Sweet potatoes with orange flesh are among the best natural sources of beta-carotene, which is converted to vitamin A in the body.
[ix]
Vitamin A is critical to a healthy immune system. "It is not surprising that
vitamin A deficiency is associated with impaired intestinal immune responses and increased mortality associated with gastrointestinal and respiratory infections," researchers wrote in Nature Reviews Immunology.
[x]
Purple sweet potatoes are also of particular interest in immune support, with polysaccharides including water-soluble polysaccharide, dilute alkali-soluble polysaccharide and concentrated alkali-soluble polysaccharide (CASP) evaluated for immune-enhancing effects.
[xi]
All three polysaccharides evaluated were found to stimulate immune responses of macrophages as well as positively regulate the subjects' adaptive immunity by enhancing immunoglobulin production. Separate research also indicates that purple sweet potato extract may address immune dysfunction by mobilizing antioxidant defenses.
[xii]
4. Anticancer Potential
Anthocyanins, a group of antioxidants found in sweet potatoes, have been widely evaluated for their
anticancer properties, particularly against colorectal, colon, bladder, breast and gastric
cancers.
[xiii],[xiv],[xv],[xvi]
Against colorectal cancer, sweet potatoes may induce cell-cycle arrest, antiproliferative and apoptotic, or cell death, mechanisms. In bladder cancer, sweet potato anthocyanins had an antitumor effect. Taiwanese purple-fleshed sweet potatoes, too, were found to have anticancer activities through their ability to inhibit the growth of cancer cell lines such as breast cancer, gastric cancer and colon adenocarcinoma.
Even sweet potato peel, usually discarded as waste, contains constituents that may help prevent various types of cancer from developing.
[xvii]
5. Diabetes Control and Prevention
Anthocyanins can also serve as a functional food for
diabetes. Antioxidants in general have been found to reduce oxidative stress due to hyperglycemia, and anthocyanins from purple sweet potatoes positively affected liver and renal activity as well as blood pressure in diabetic animal models.
[xviii]
Read more at:
GreenMedInfo.com
 Parler
Parler Gab
Gab